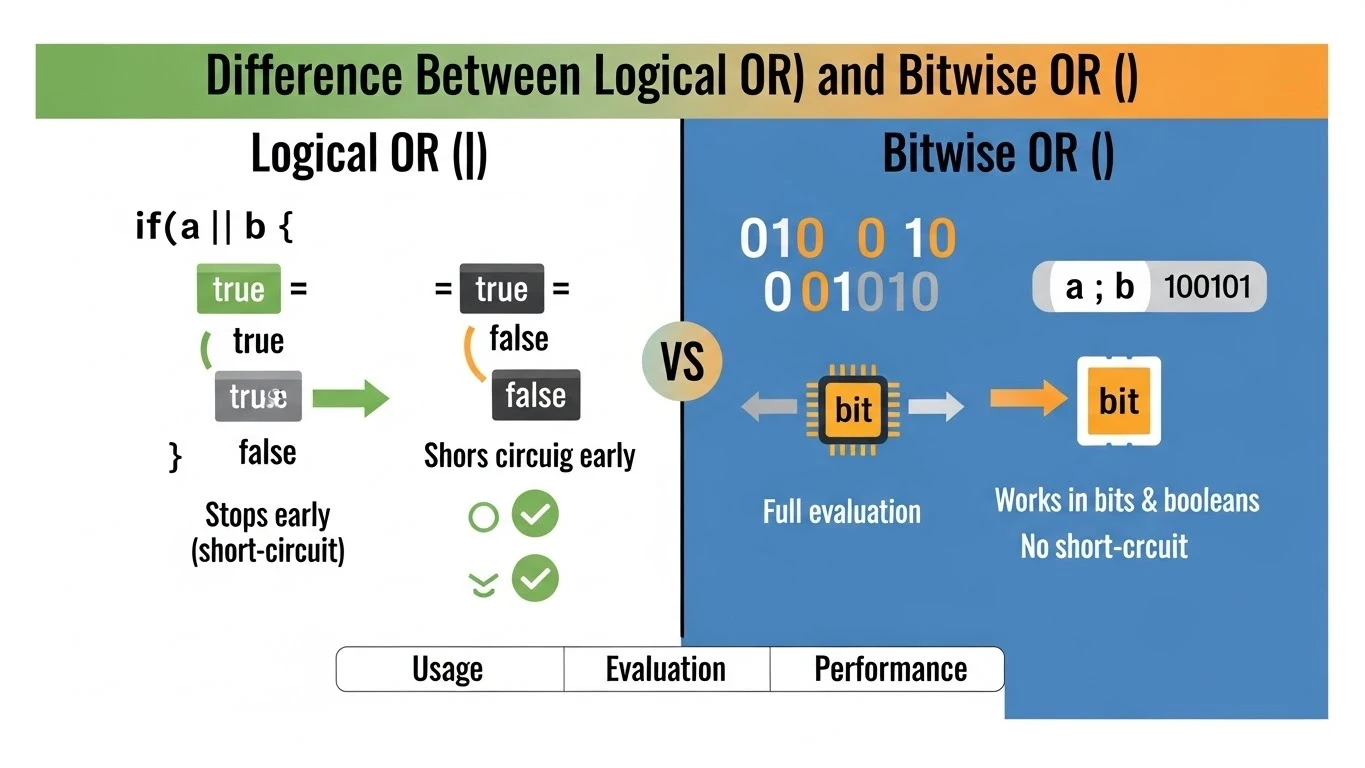
Many Java learners search for “Java OR operator” because they feel confused between logical OR (||) and bitwise OR (|). Both symbols look similar, but they work very differently. Beginners often mix them up in exams, interviews, and real programs.
The OR operator is used when you want one condition or value to be true. In simple words, OR means “this OR that”. Java provides two types of OR operators, and choosing the wrong one can cause errors or wrong results.
This article clears all confusion. You will learn what the Java OR operator is, its types, syntax, rules, real examples, common mistakes, and interview tips. By the end, you will know exactly when to use || and when to use |.
If you are a student, job seeker, or beginner, this guide is written just for you—clear, simple, and practical.
Java OR Operator ; Quick Answer
In Java, the OR operator is used to combine conditions or values.
Java has two OR operators:
| Operator | Name | Used For |
| ` | ` | |
| ` | ` | Bitwise OR |
Example:
if (age > 18 || hasLicense) {
System.out.println(“You can drive”);
}
If any one condition is true, the result is true.
Types of OR Operators in Java
Java provides two different OR operators based on usage.
1. Logical OR Operator (||)
2. Bitwise OR Operator (|)
Let’s understand both one by one.
Logical OR Operator (||) in Java
What is Logical OR?
The logical OR (||) operator is used with boolean values (true or false).
Rule:
If any one condition is true, the result is true.
Syntax
condition1 || condition2
Truth Table for Logical OR
| Condition A | Condition B | Result |
| true | true | true |
| true | false | true |
| false | true | true |
| false | false | false |
Example 1: Simple Example
boolean isAdult = true;
boolean hasID = false;
System.out.println(isAdult || hasID);
Output:
true
Because one condition is true.
Example 2: Using OR in if Statement
int marks = 35;
if (marks >= 33 || marks == 32) {
System.out.println(“Pass”);
}
Even if one condition matches, the block runs.
Short-Circuit Behavior (Important)
The logical OR (||) is a short-circuit operator.
👉 If the first condition is true, Java does not check the second one.
Example
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
if (a > 5 || b > 1) {
System.out.println(“Hello”);
}
Java never checks b > 1 because a > 5 is already true.
More information: Is It Carma or Karma? Explained Simply 2026
Bitwise OR Operator (|) in Java

What is Bitwise OR?
The bitwise OR (|) operator works on binary values (bits).
It compares each bit of two numbers.
Rule:
If any bit is 1, the result bit is 1.
Syntax
number1 | number2
Bitwise OR Truth Table
| Bit A | Bit B | Result |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
System.out.println(result);
Binary calculation:
0101
0011
—-
0111 = 7
Output:
7
Example 2: Bitwise OR with Booleans
boolean x = false;
boolean y = true;
System.out.println(x | y);
Output:
true
⚠️ Even though this works, | is not recommended for conditions.
Difference Between || and | in Java
| Feature | Logical OR (||) | Bitwise OR (|) |
|——|——————|—————-|
| Works on | Boolean | Bits & Boolean |
| Short-circuit | Yes | No |
| Checks second condition | Only if needed | Always |
| Used in conditions | Yes | No (avoid) |
| Performance | Faster | Slower |
When to Use Logical OR (||)
Use || when:
- Writing if, while, or for conditions
- Checking multiple conditions
- You want better performance
- You want short-circuit behavior
Example:
if (isLoggedIn || isAdmin) {
accessGranted();
}
When to Use Bitwise OR (|)
Use | when:
- Working with binary numbers
- Using flags or masks
- Low-level programming
Common Mistakes with Java OR Operator
Mistake 1: Using | instead of ||
❌ Wrong:
if (a > 5 | b < 10)
✅ Correct:
if (a > 5 || b < 10)
Mistake 2: Expecting Short-Circuit with |
| always checks both sides.
Mistake 3: Using OR instead of AND
Students confuse OR (||) with AND (&&).
Java OR Operator in Real-Life Examples
Example 1: Login System
if (emailVerified || phoneVerified) {
allowLogin();
}
Example 2: Discount System
if (isMember || cartValue > 5000) {
applyDiscount();
}
Example 3: Exam Eligibility
if (attendance >= 75 || medicalCertificate) {
allowExam();
}
Java OR Operator in Interviews
Common Interview Questions
Q1: Difference between | and || in Java?
👉 || is logical OR with short-circuit. | is bitwise OR.
Q2: Which OR operator is faster?
👉 Logical OR (||)
Q3: Can | be used in if condition?
👉 Yes, but not recommended.
Q4: What is short-circuit in Java?
👉 Java stops checking when result is already known.
Java OR Operator – Comparison Table
| Operator | Type | Use Case | Example |
| ` | ` | Logical OR | |
| ` | ` | Bitwise OR | Binary ops |
FAQs
1. What is OR operator in Java?
It combines conditions and returns true if one condition is true.
2. How many OR operators are in Java?
Two: || and |.
3. Is || better than |?
Yes, for conditions.
4. Can OR operator work with integers?
Only bitwise OR (|) works with integers.
5. Does OR operator stop execution?
Logical OR (||) may stop checking second condition.
6. Is OR operator used in loops?
Yes, with conditions.
7. Is OR operator important for interviews?
Yes, very important.
Conclusion
The Java OR operator is simple once you understand its types. Java provides logical OR (||) for conditions and bitwise OR (|) for binary operations. Most beginners struggle because both symbols look similar, but their behavior is very different.
For everyday programming, always use logical OR (||) in if, while, and for statements. It is faster, safer, and easier to read. Use bitwise OR (|) only when working with numbers at the bit level.
If you remember one rule, remember this:
👉 Conditions = ||, Binary = |
Mastering this concept will help you write better Java code, avoid mistakes, and perform well in exams and interviews.

I am an English author who loves words and their meaning. Writing is not just my work, it is my passion. I write to make English simple, clear, and easy to understand for everyone. My focus is on real language, real mistakes, and real learning. Every article I write comes from research, experience, and a love for honest writing. My goal is simple: help readers feel confident with English.